

The net dipole moment of a molecule is zero when two equal and opposing charges are present in the molecule. To begin, let's review the notion of dipole moment, which is a number that is measured in a molecule to determine the partial charges present between the two atoms or groups present in that molecule. The structure of the molecule BF 3 can be drawn to get a sense of the BF 3 dipole moment value contained in the molecule. This yields a dipole moment of 1.49D as a consequence.Ī molecule's dipole moment definition is a phrase that defines the two opposing charges within the molecule that are separated by a distance. With three N-H bonds and a lone pair on the nitrogen atom, NH 3 has a pyramidal structure. Ammonia is polar due to the existence of both positive and negative charges on the molecule, and so has a net dipole moment.
MOLECULAR DIPOLE MOMENT DEFINITION PLUS
This provides nitrogen a partial negative charge (shown by a minus sign on N) and hydrogen a partial positive charge (represented by a plus sign on H) (which is denoted by a plus sign on each H). Because nitrogen attracts electrons more strongly than hydrogen, the electrons they share are attracted to nitrogen rather than hydrogen. One nitrogen atom is covalently linked to three hydrogen atoms in ammonia. Dipole moments cancel each other out in a single plane, resulting in a net dipole moment of zero. The electrons in a covalent bond connecting two. This is due to the fact that BH 3 has a symmetrical structure, with the three B-H bonds arranged at a 120-degree angle to one another. The term dipole moment can be defined either with respect to chemical bonds or with respect to molecules. The dipole moment of boron trihydride (BH 3) is zero, whereas that of ammonia (NH 3) is 1.49D. The molecular dipole moment is responsible for the behavior of matter in the presence of an external electric field.
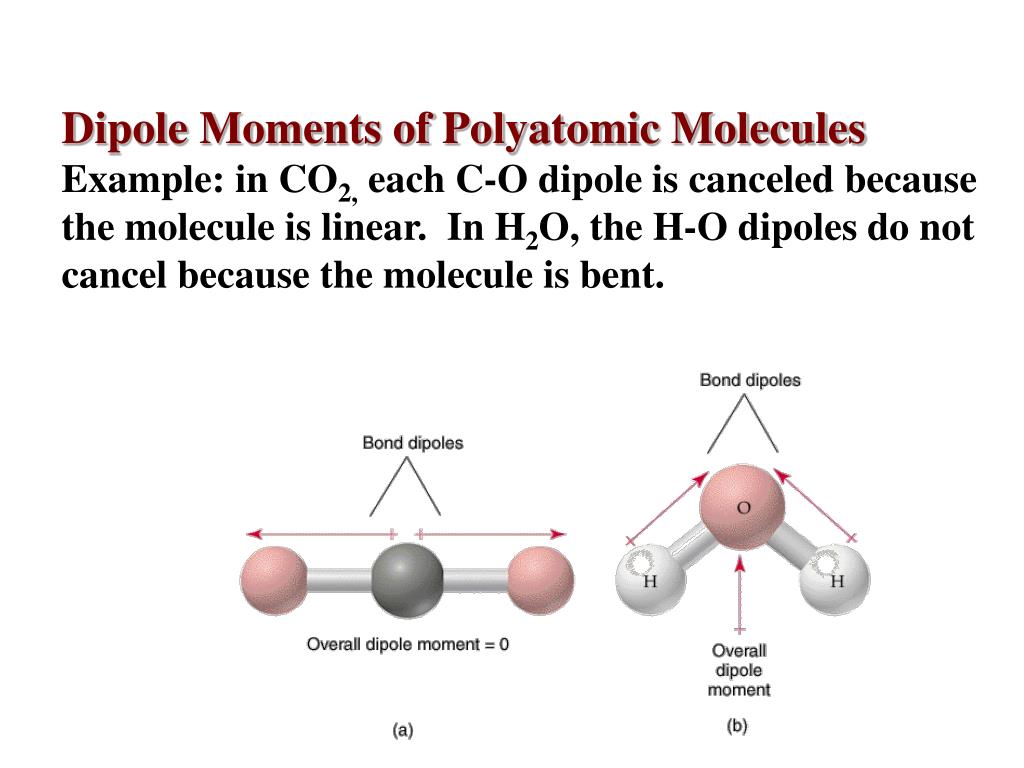
The dipole moment of the C=O bond (2.3D) on one side of the molecule is negated by that on the opposite side of the molecule due to the linear structure of the molecule, resulting in net zero dipole moment. The dipole moment of the triatomic CO 2 (carbon dioxide) molecule is zero. The dipole moment of the HCl molecule in the diatomic molecule is the same as the dipole moment of the HCl link, which is 1.03D.

NCERT notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 2 Structure of Atom.The bond dipole moment in chemistry can be used to depict the movement of electrons. When two atoms with different electronegativities collide, the electrons tend to migrate away from their original locations in order to approach the more electronegative atom. The arrows used to illustrate dipole moments in chemistry start at the positive charge and stop at the negative charge. The bond dipole moment (µ) is a vector quantity with the same direction as the bond axis. ? → magnitude of the partial charges ? + and ? –, In a chemical bond between two atoms with differing electronegativities, the bond dipole moment formula can be written as, Where, C stands for Coulomb and m for metre. It is measured in Debye units, which are represented by the letter ‘D.' Mathematically, dipole moment formula can be written as,ĭipole Moment=ChargeQ*Distance of separation(d) Therefore, the net dipole moment of CO 2 is zero.By the dipole moment definition, the dipole moment formula is the product of magnitude of charge and the distance between the positive and negative charge centres. However, as the structure is linear, the dipole moment of one bond is canceled by the other. There are dipole moments due to the C-O bonds. Carbon dioxide (CO 2)ĬO 2 has a linear structure, O=C=O, and displays symmetry. Based on these facts, let us look at the dipole moments of a few molecules. Second, its shape should be such that the individual bond dipoles do not cancel out. There are two critical considerations for a molecule to have a dipole. The difference in sizes of the two atoms.R i: distance of the i-th atom from a reference pointĪside, there are other factors that the total molecular dipole moment depends upon. The dipole moment () is defined as the product of the magnitude of the charge, e, and the distance separating the positive and negative charges, l: el. Therefore, the net moment is the vector addition of the individual moments. However, the molecule’s overall dipole moment will depend upon the magnitude and direction of the individual bond dipole moments. Each pair of atoms will have a bond dipole moment due to chemical bonding, represented by magnitude and direction.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
